SQL Load Optimization
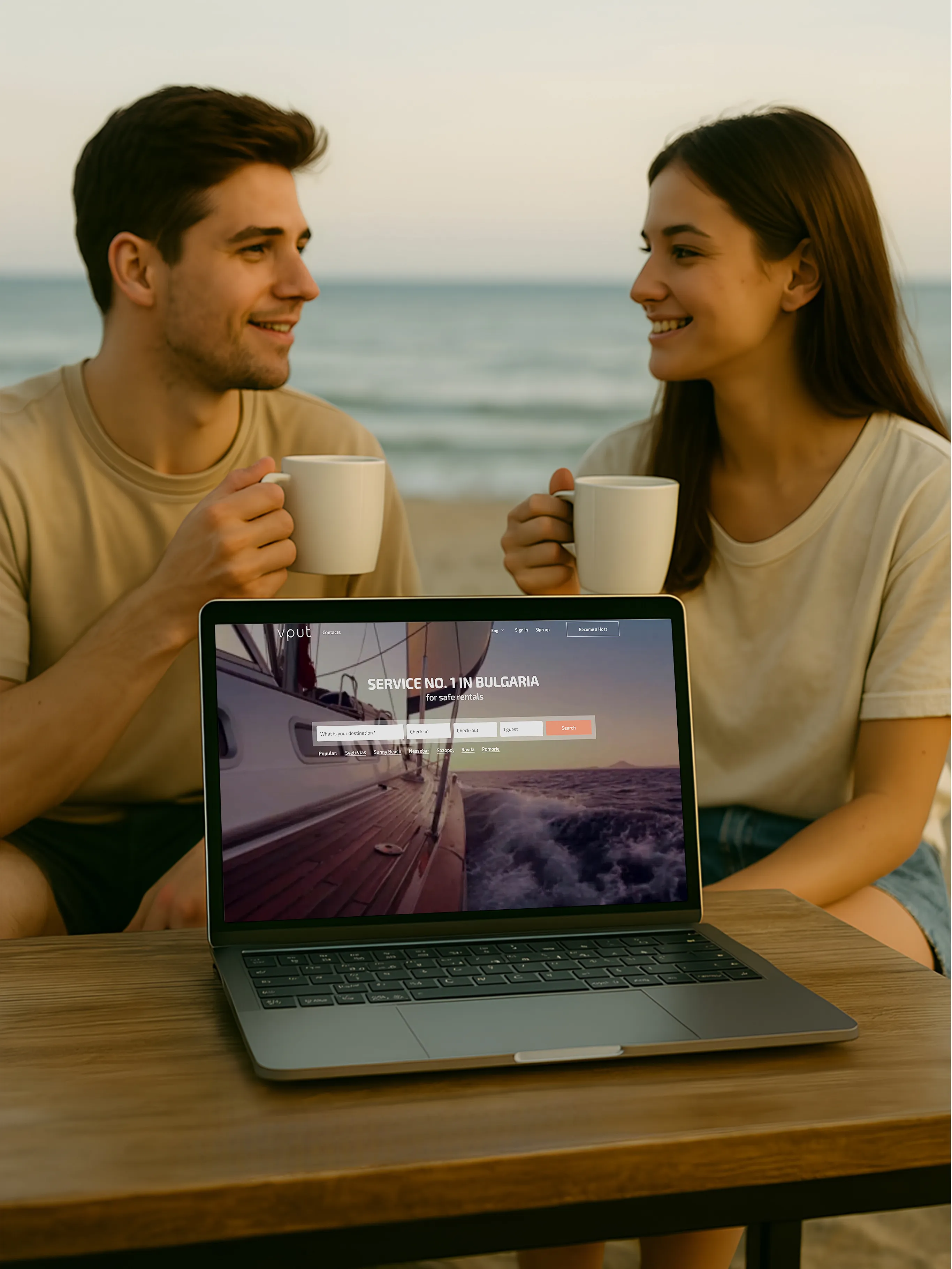
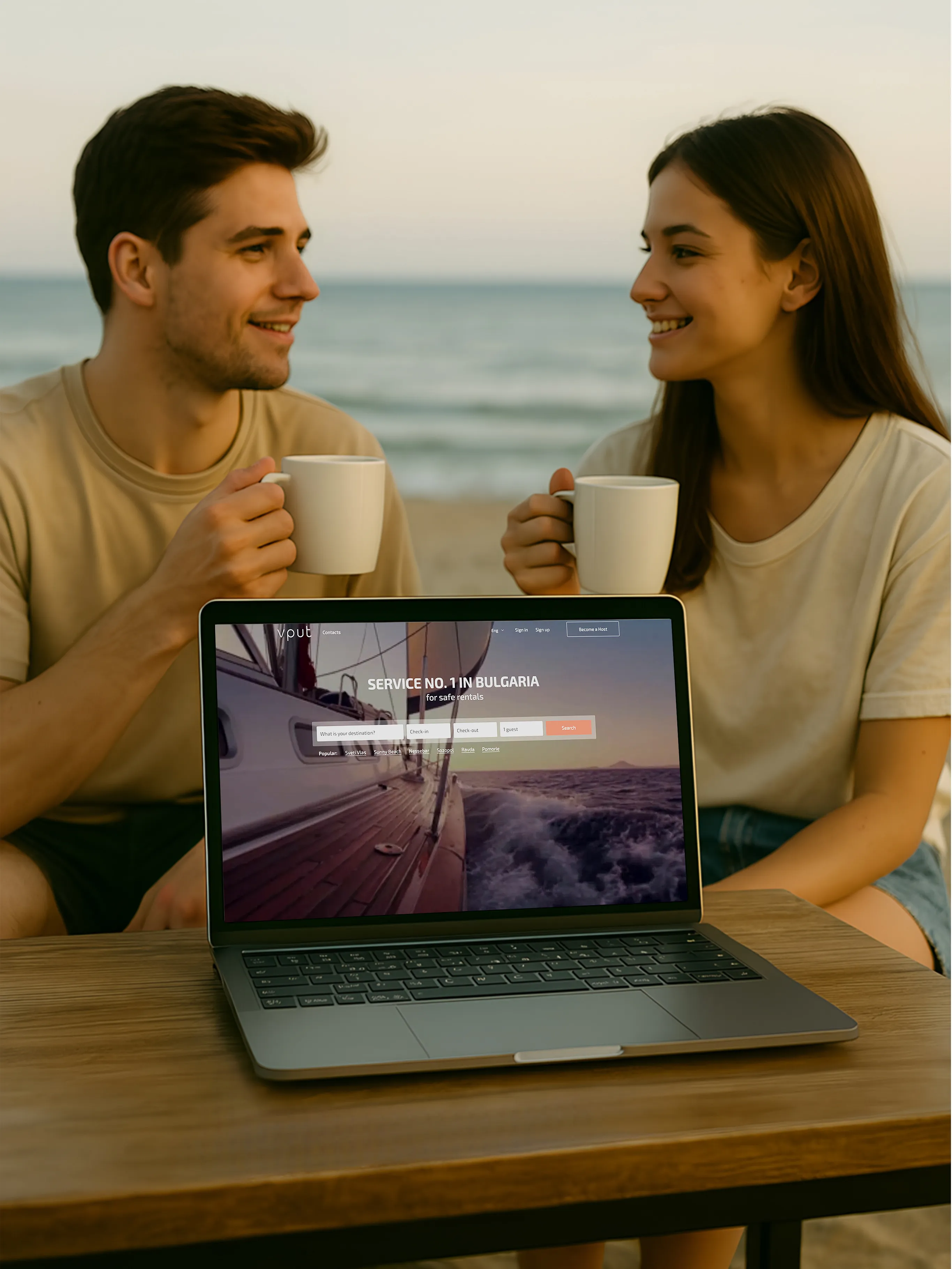
Major E-commerce Platform
Introduction
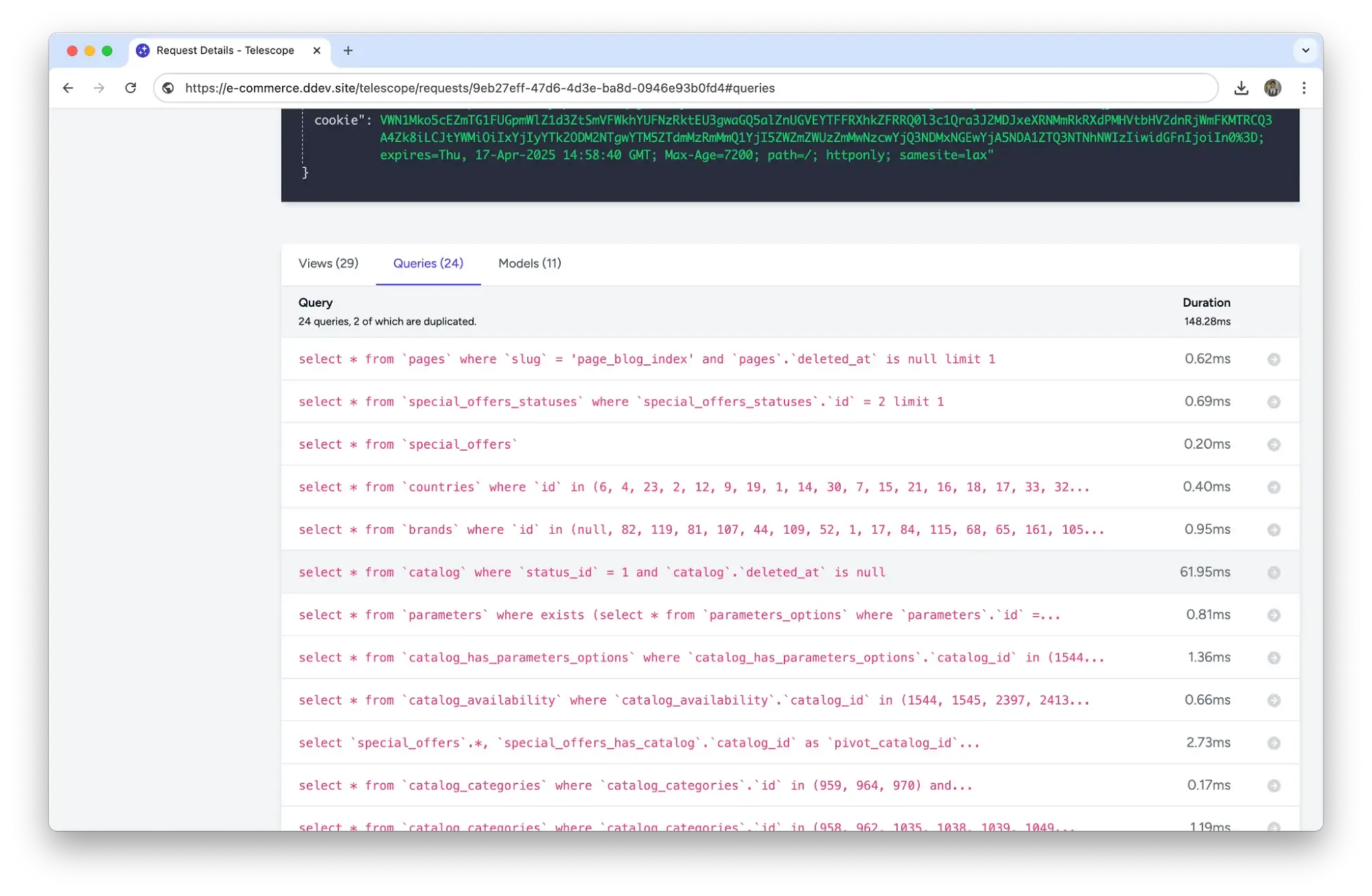
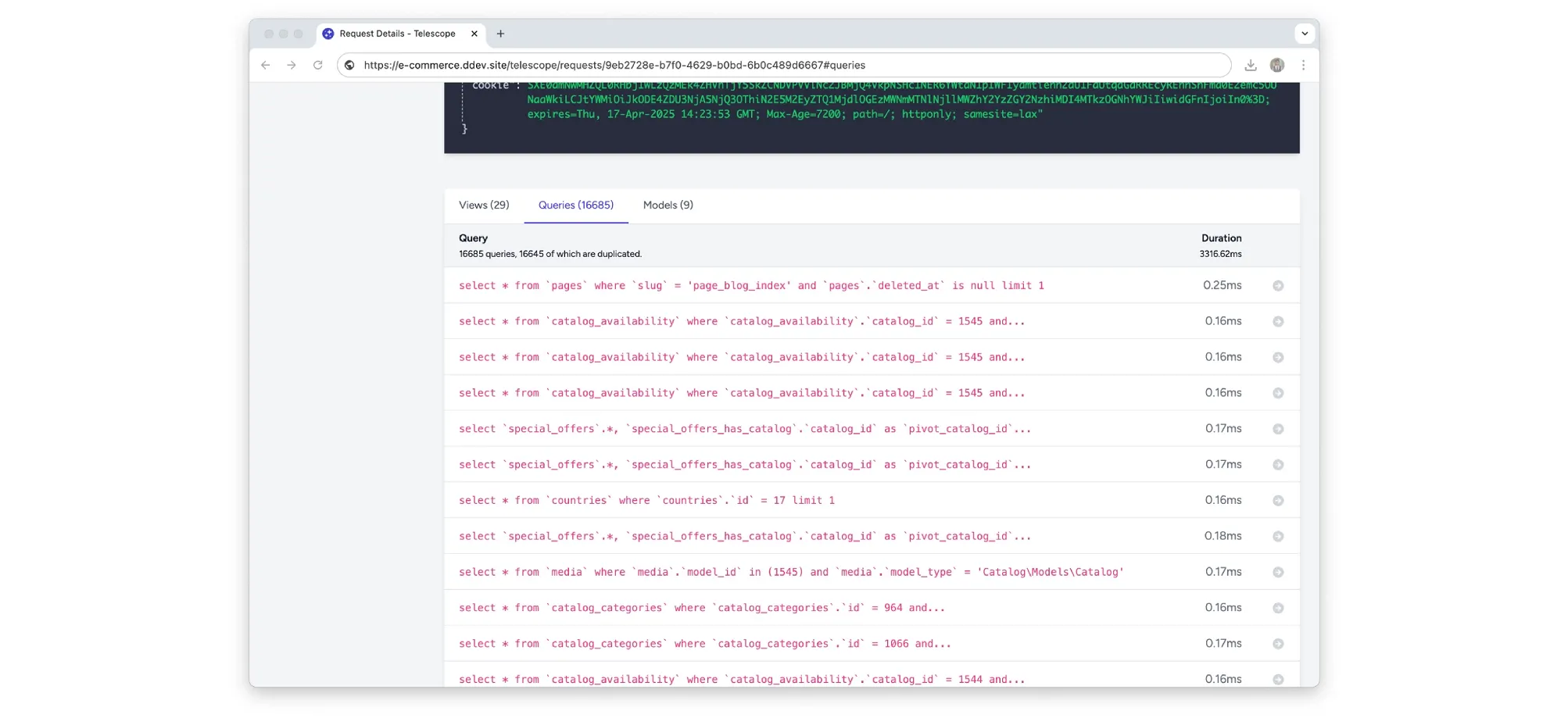
A client approached us with a task: speed up the loading time of a key website page that was experiencing delays of several seconds. An initial audit revealed the root cause — excessive load on the database: opening the page triggered over 16,000 SQL queries.
This load not only impacted performance but also posed a risk of outages under increased traffic. The task was to optimize the system within a tight timeframe without affecting core business logic or disrupting other parts of the website.
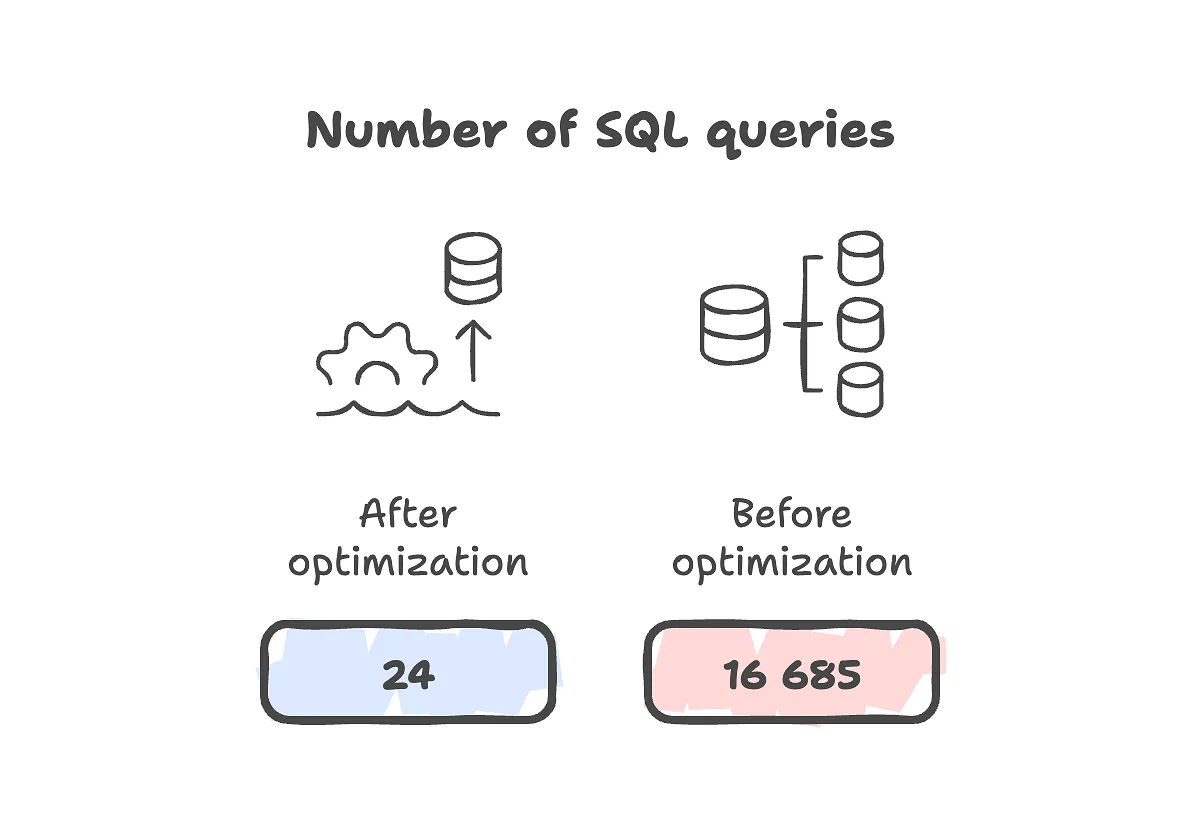
Our team performed a targeted optimization of the data loading architecture and achieved a result: just 24 queries instead of 16,685. The entire process took no more than an hour and a half.
System Overview
The project is a multifunctional e-commerce platform built on Laravel 10 using Eloquent ORM, with MySQL as the database. The frontend is based on Blade, with partial use of Vue.js.
The problematic page displays a product catalog. Each item includes images, characteristics, filter parameters, brand info, availability status, and personalized user data (e.g., favorites).
Due to high data interconnectivity and the lack of optimization mechanisms, the number of SQL queries grew exponentially.
The issue was not the volume of data, but how it was retrieved: eager loading was not used, resulting in the N+1 problem, where additional queries are executed for every record to fetch related data.
With profiling tools enabled (Laravel Debugbar, SQL logging), we identified 16,685 queries being executed during a single page load. Key reasons included:
- Related entity queries executed inside loops
- Undefined or unused relationships between models
- Template logic accessing relationships without preloading
The client also set strict requirements:
- No changes to business logic or the API
- The solution must be scalable
- Full adherence to Laravel best practices, with no “hacky” workarounds like manual data aggregation
Solution: Implementing Eager Loading and Optimizing Models
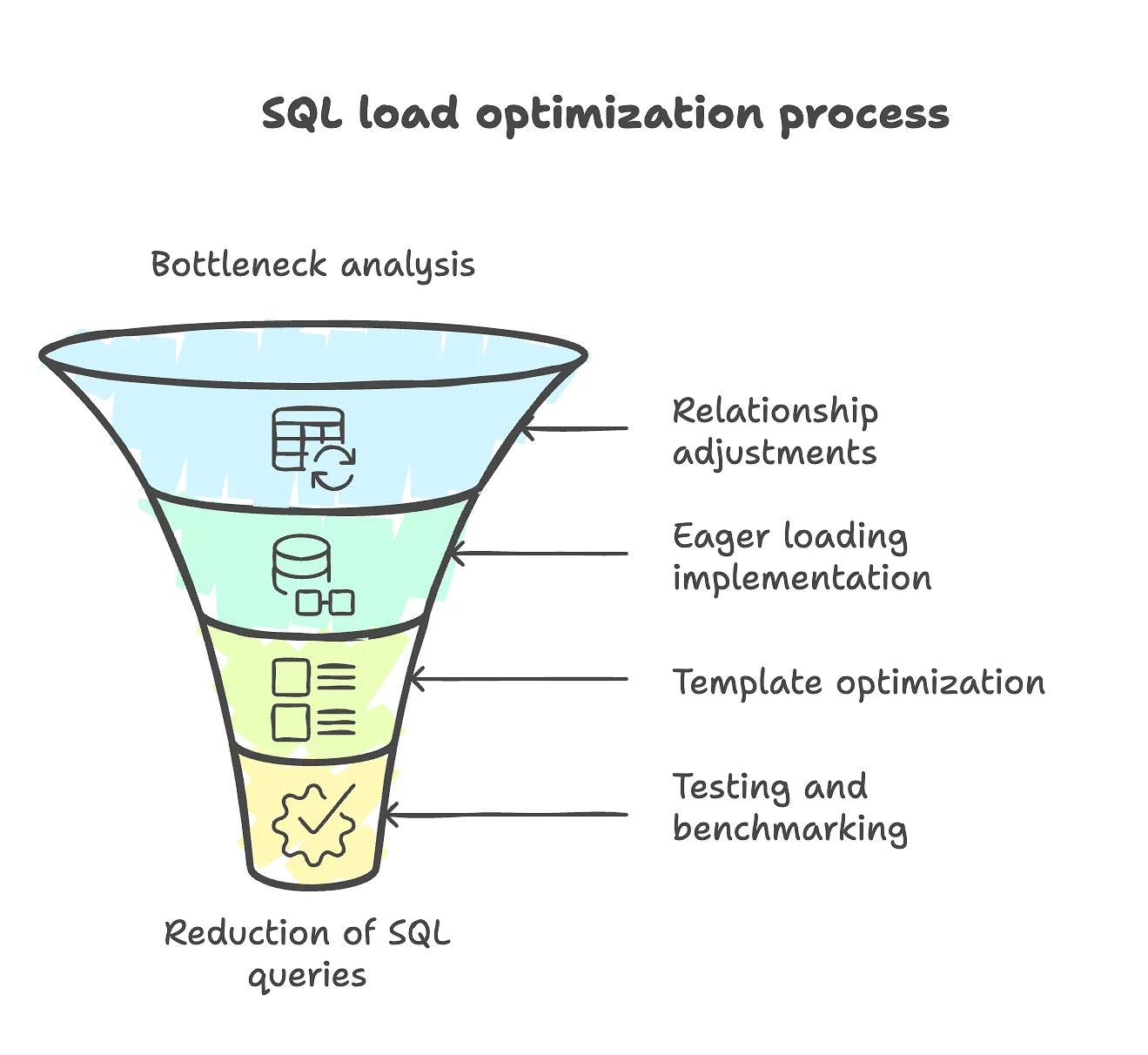
The optimization was carried out in several key areas:
Bottleneck Analysis
All involved models, controller logic, and templates were reviewed to identify performance issues.
Refining Model Relationships
Relationships like hasMany, belongsTo, hasOne, and morphMany were clarified in the models, making table relationships explicit and enabling eager loading.
Eager Loading Implementation
Wherever deferred relationship access was previously used, with() and load() calls were introduced to fetch all necessary data in a single, joined query.
Example:
Product::with(['images', 'brand', 'filters', 'favorites'])->get();
Template and Presentation Logic Optimization
Blade templates were revised: relationship access inside loops was eliminated, rendering logic was simplified, and redundant queries removed.
Testing and Benchmarking
After implementation, load tests and a second SQL audit were conducted. Result: only 24 queries were executed for a full page load.